How You Hear Northland Audiology
labeling the ear by nielsejo86 185,927 plays 12 questions ~30 sec English 12p More 119 3.89 (you: not rated) Tries Unlimited [?] Last Played December 4, 2023 - 03:07 am There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. Remaining 0 Correct 0 Wrong 0 Press play! 0% 0:00.0 Other Games of Interest

Outer Ear Anatomy Outer Ear Infection & Pain Causes & Treatment
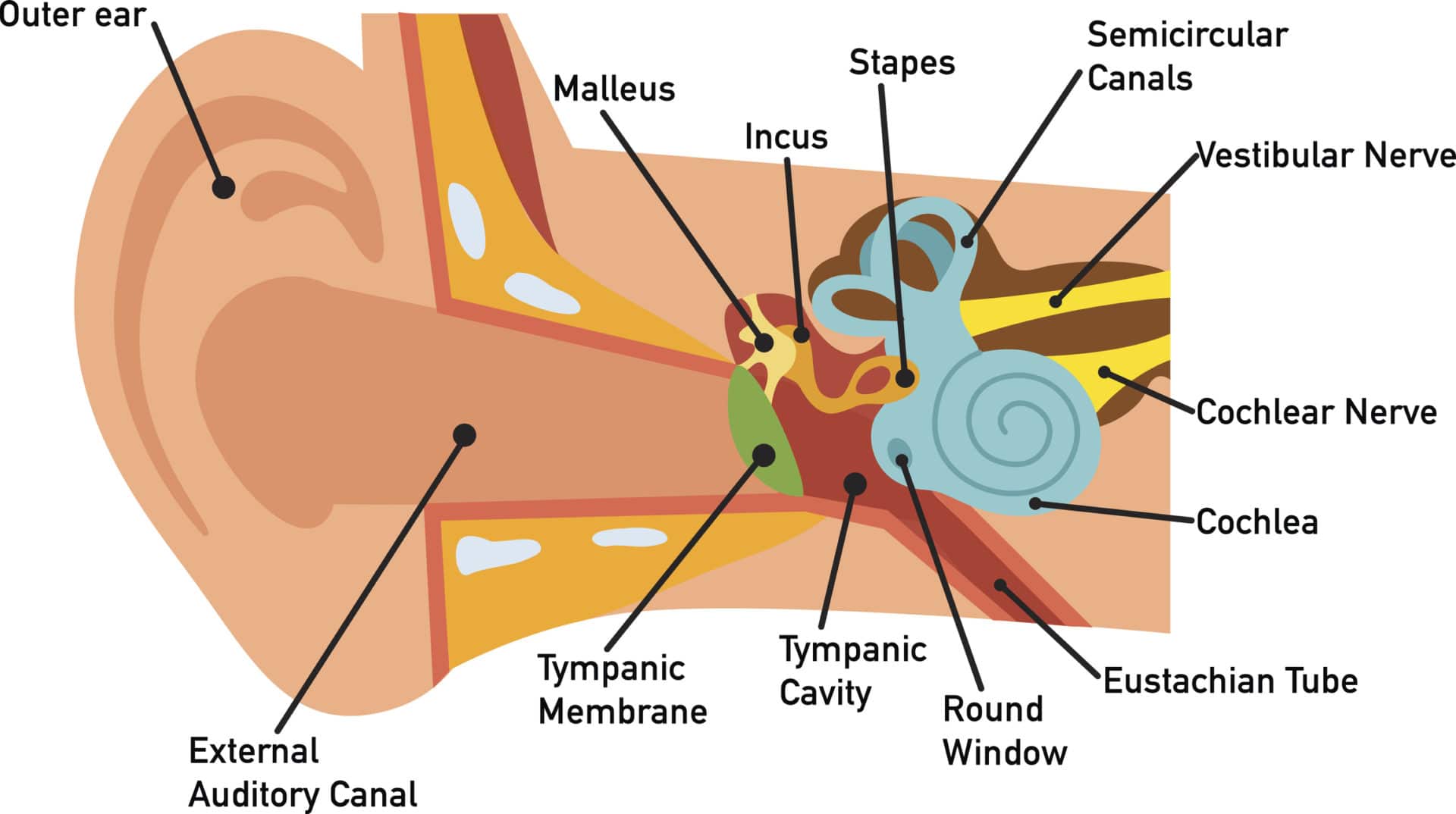
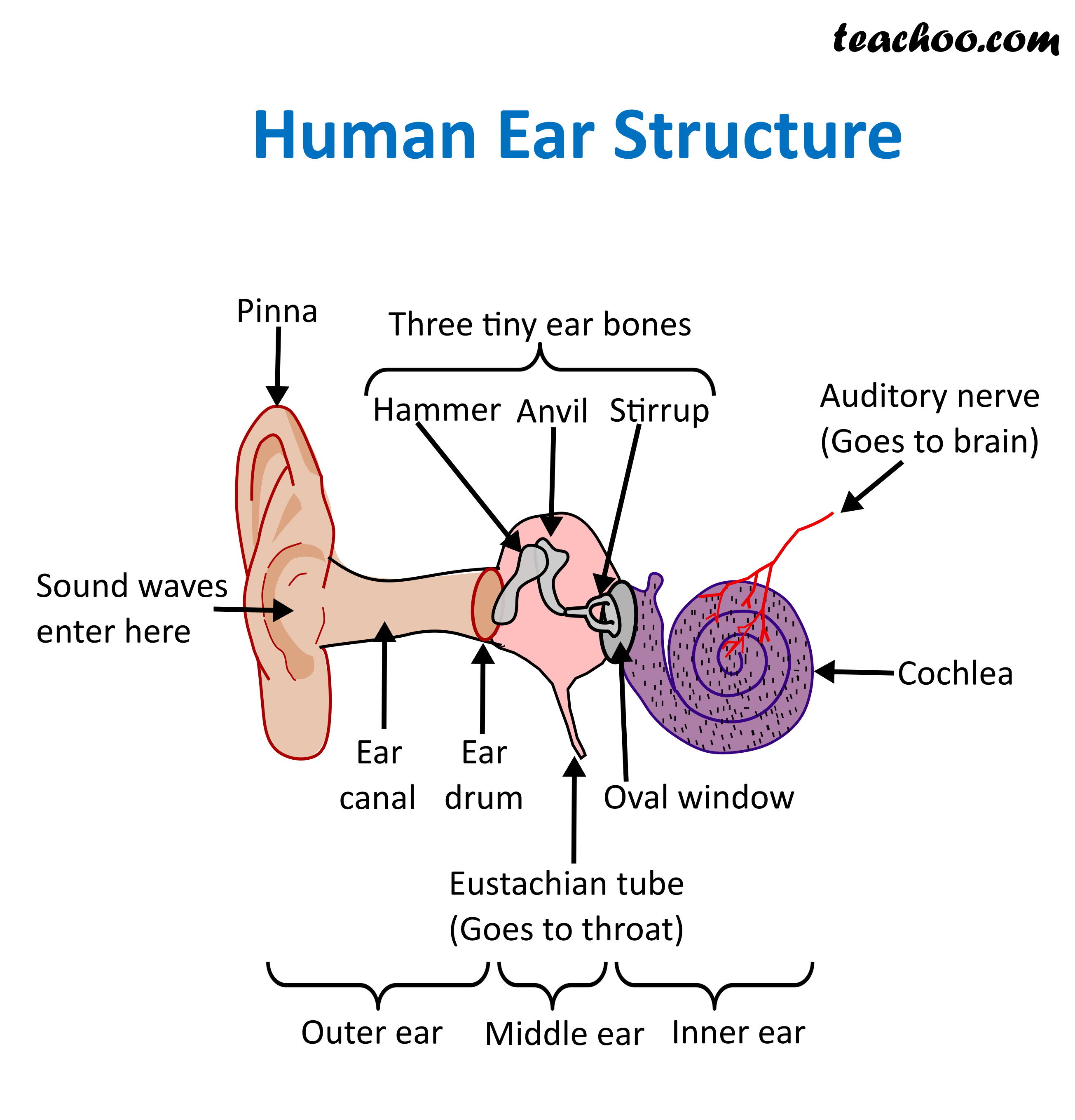
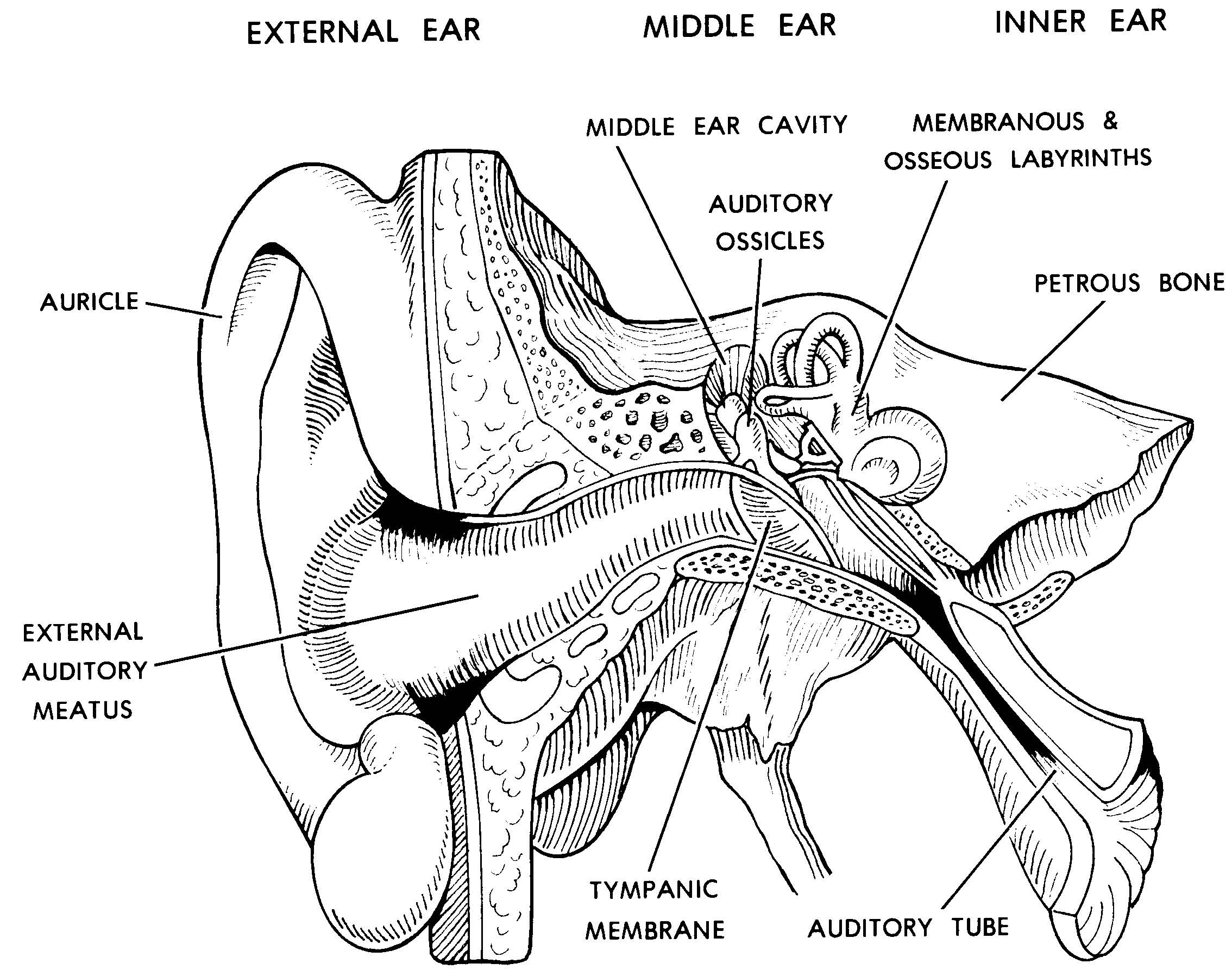
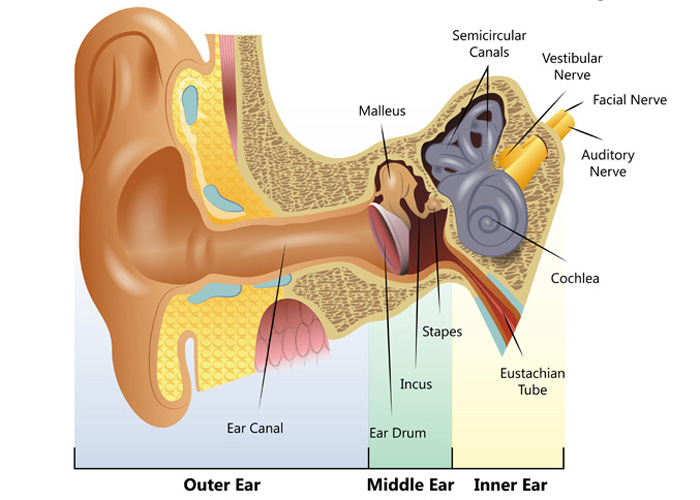
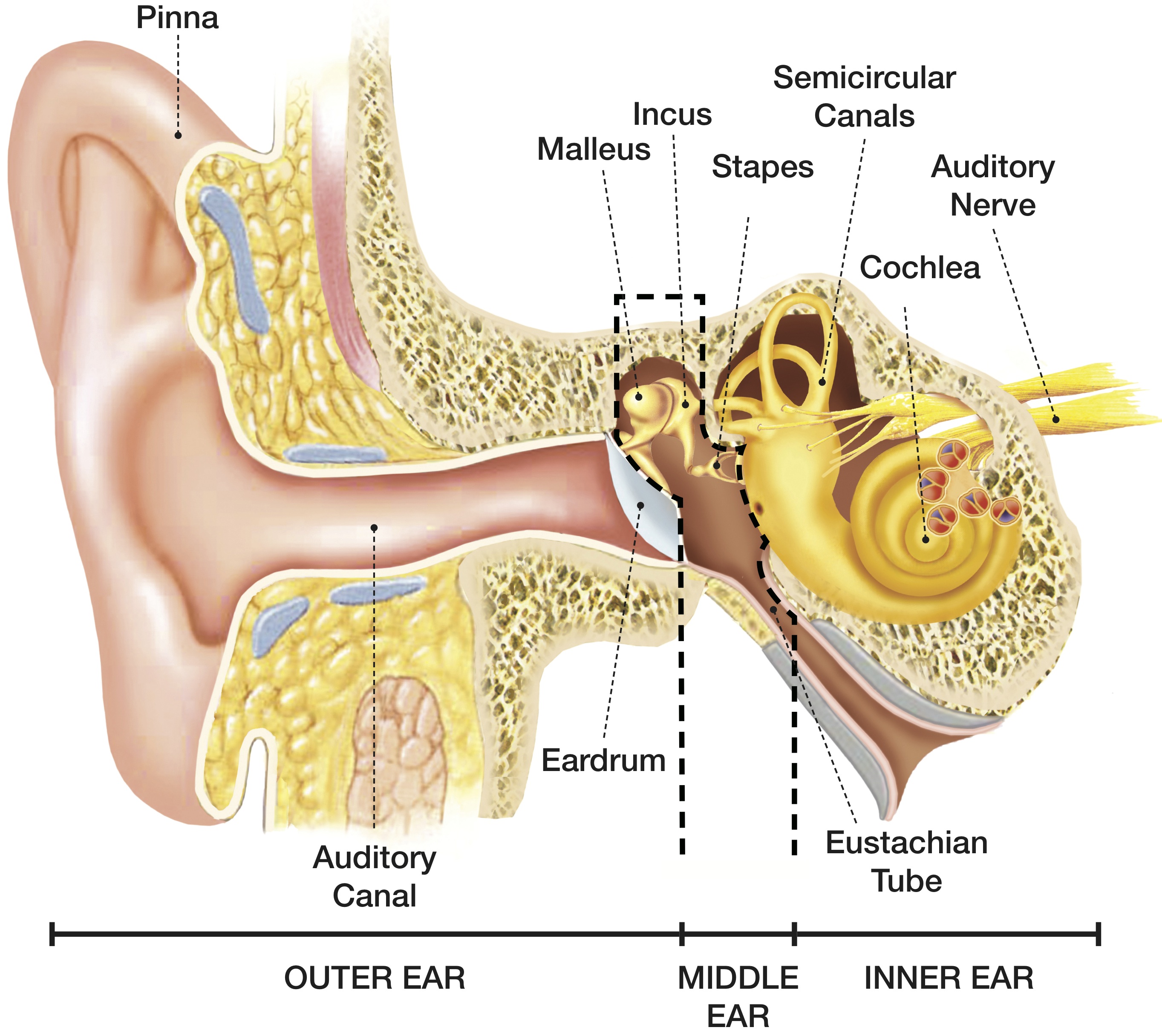
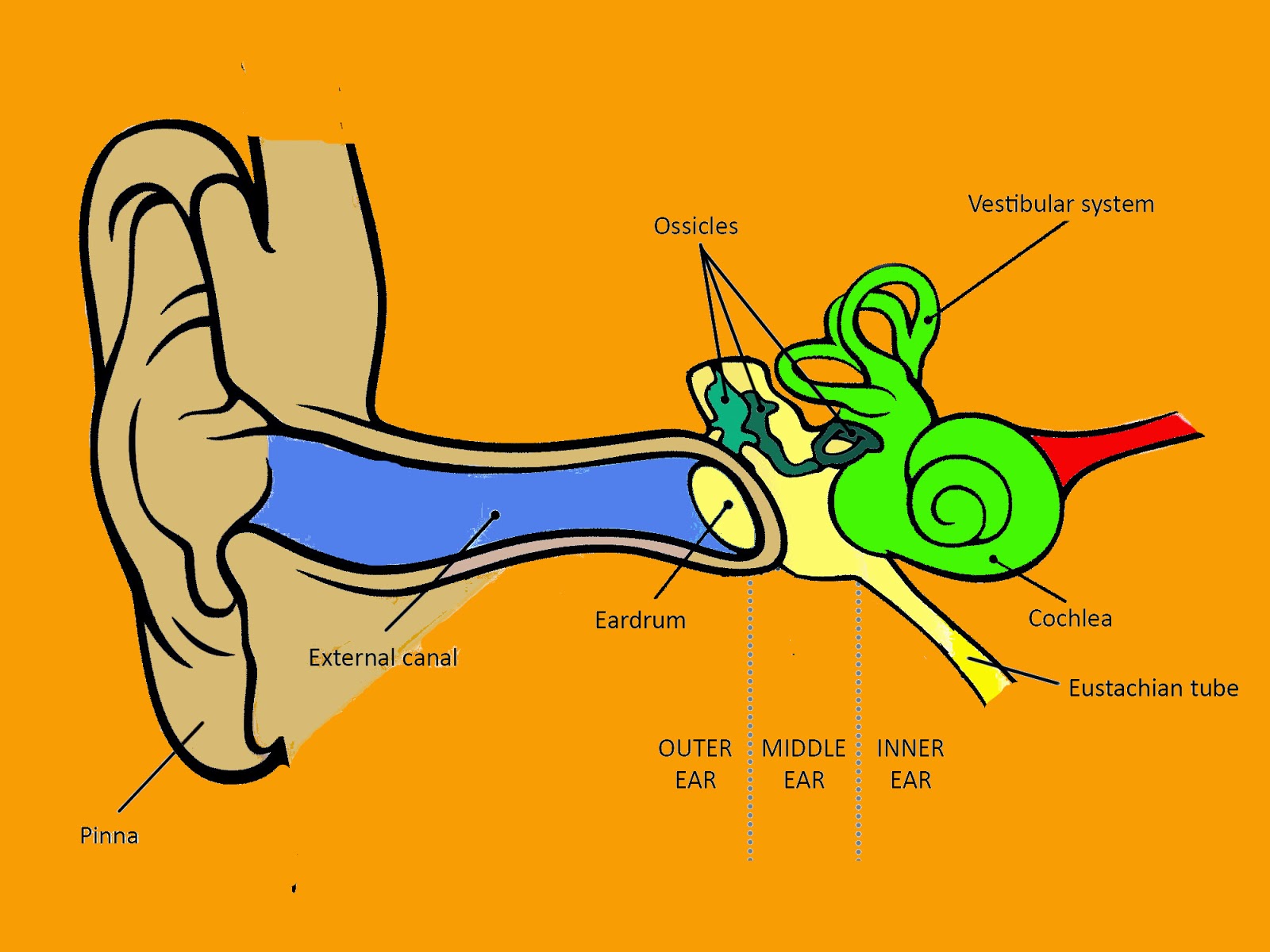
The middle ear includes the eardrum, malleus, incus, and stapes. The inner ear includes semicircular canals, eustachian tube, cochlea, and vestibule and auditory nerves.">.

How The Ear Works
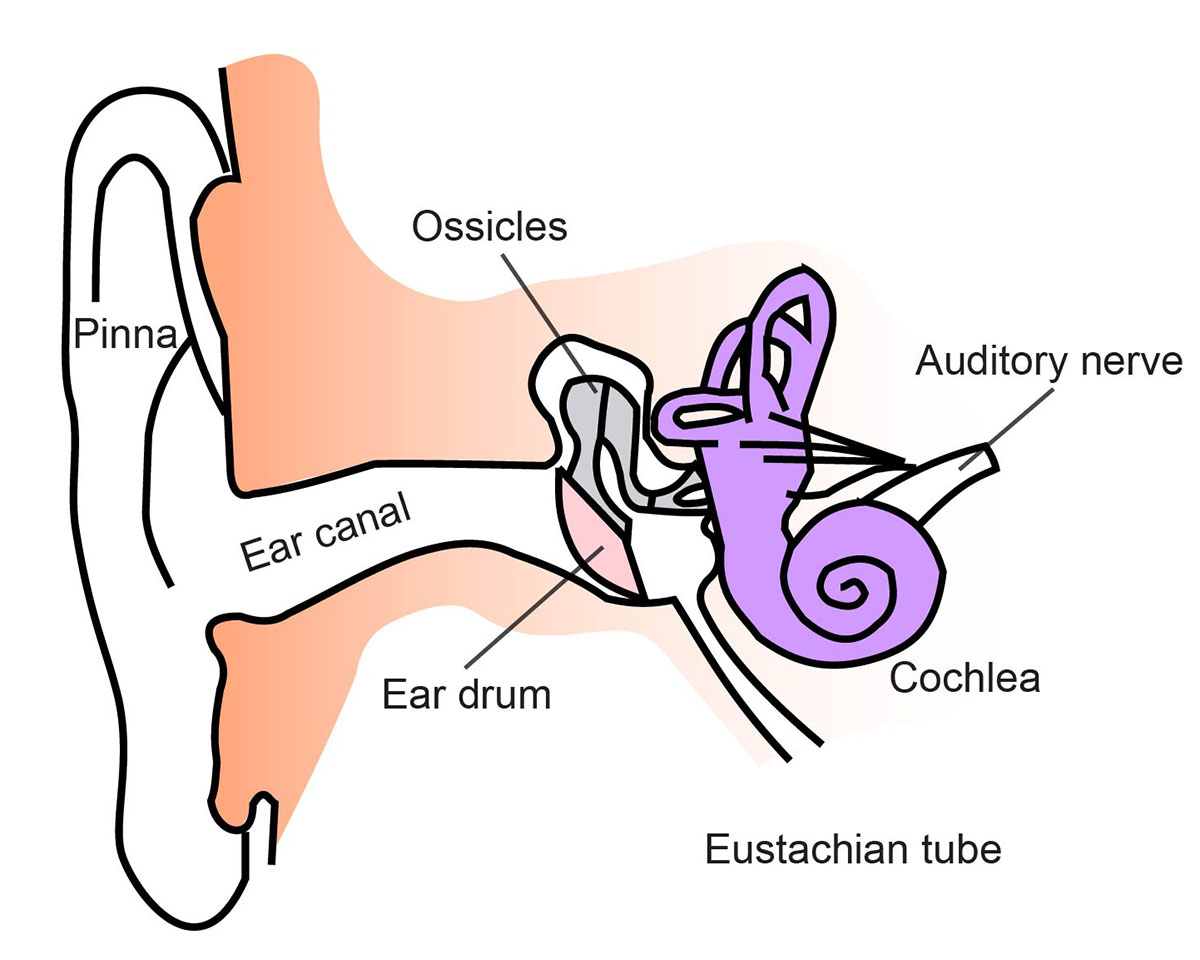
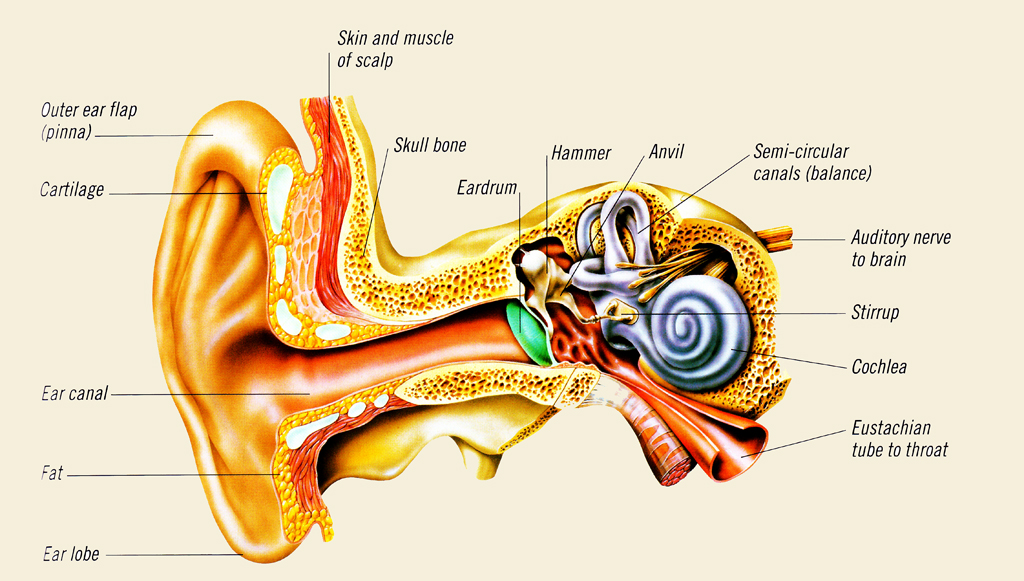
So as the air vibrates even the ear drum starts vibrating. Just like the skin of a drum. And as you can, the ear drum also separates the outer ear from the middle ear. This brings us to the middle ear. The middle ear consists of the three tiniest bones of the human body. And they're together the are called the ossicles. And they have pretty.
Structure and Function of Human Ear with Diagram Teachoo
EAR CANAL The ear canal starts at the outer ear and ends at the ear drum. The canal is approximately an inch in length. The skin of the ear canal is very sensitive to pain and pressure. Under the skin the outer one third of the canal is cartilage and inner two thirds is bone. EAR DRUM
Ear Anatomy Causes of Hearing Loss Hearing Aids Audiology
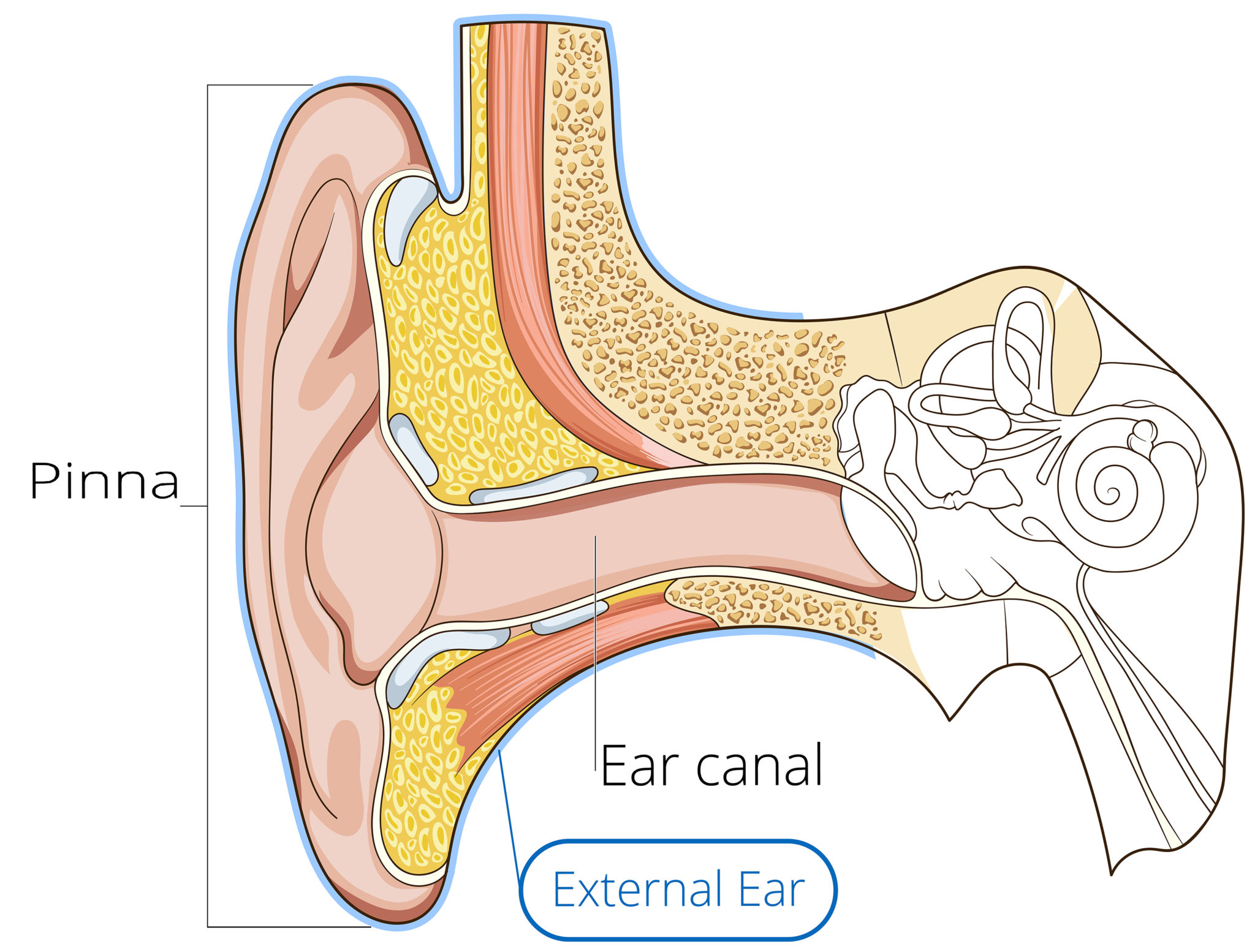
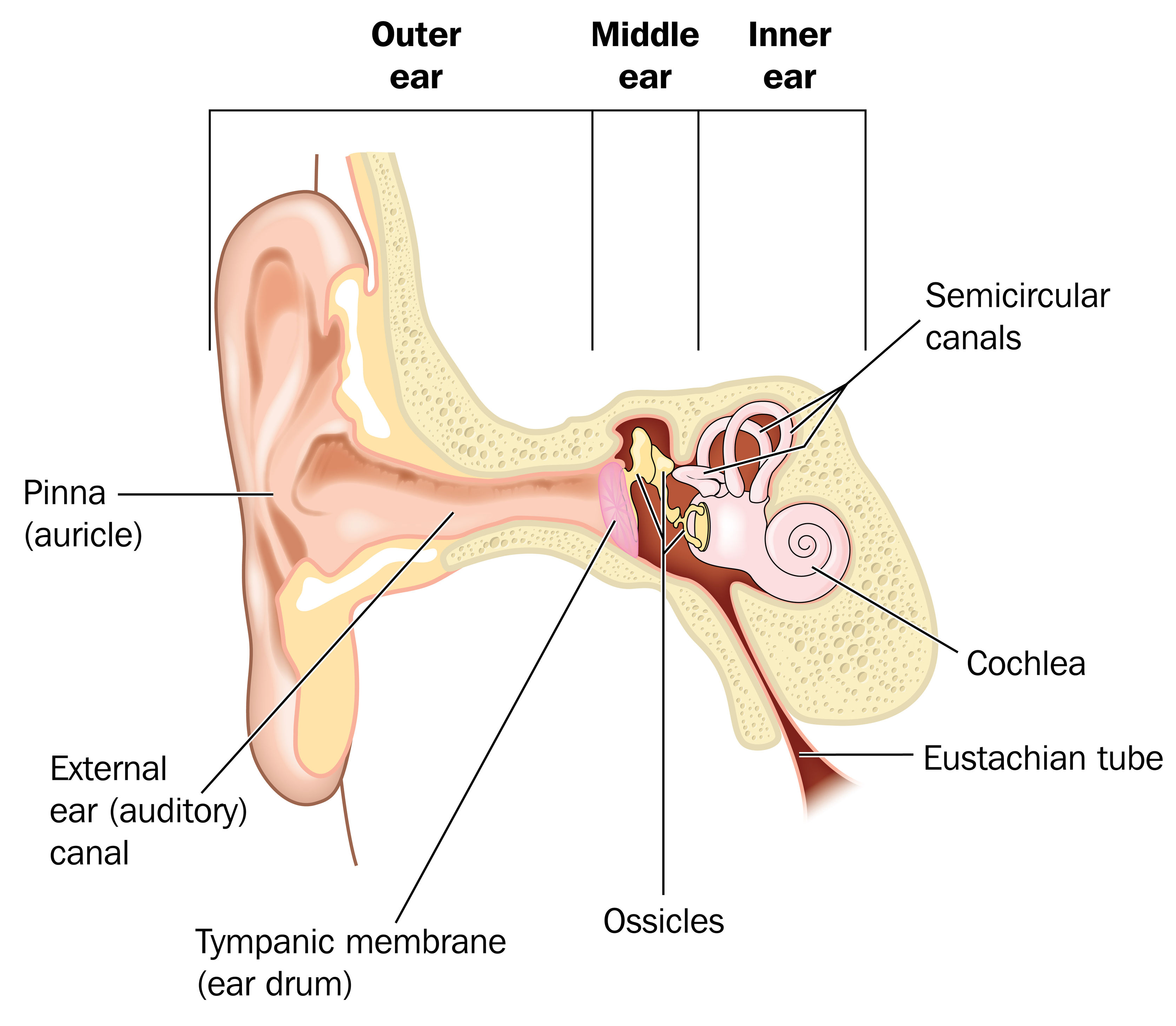
The outer ear consists of the visible portion called the auricle, or pinna, which projects from the side of the head, and the short external auditory canal, the inner end of which is closed by the tympanic membrane, commonly called the eardrum. The function of the outer ear is to collect sound waves and guide them to the tympanic membrane.
ear anatomy diagram labeled
The ear canal, or auditory canal, is a tube that runs from the outer ear to the eardrum. The ear has outer, middle, and inner portions. The ear canal and outer cartilage of the ear make.
Images 11. Nervous System Basic Human Anatomy
The inner ear is the innermost part of the ear and consists of the cochlea, auditory nerve, vestibule and semicircular canals. The inner ear is a maze of tubes and passages, referred to as the labyrinth. The inner ear is mainly responsible for balance and detecting sound. The cochlea contains the cells responsible for hearing, the auditory.
Discovering Something New ongoing learning How the ear works
Ear anatomy can vary. In addition to normal and relatively minor differences, there are a number of more significant and impactful variants. For instance, on the auricle, attachment—or lack thereof—of the earlobe to the face is a frequently seen genetic variation, with attached earlobes seen in anywhere from 19% to 54% of the population..
Ear Diagram Helix Human Anatomy diagram
outer ear canal - the tube through which sound travels to the eardrum. pinna - (also called the auricle) the visible part of the outer ear. It collects sound and directs it into the outer ear canal. semicircular canals - three loops of fluid-filled tubes that are attached to the cochlea in the inner ear. They help us maintain our sense of balance.
Understanding how the ear works Hearing Link Services
A brief description of the human ear along with a well-labelled diagram is given below for reference. Well-Labelled Diagram of Ear The External ear or the outer ear consists of Pinna/auricle is the outermost section of the ear. The external auditory canal links the exterior ear to the inner or the middle ear.
Ear infections explained Dr Mark McGrath
The parts of the ear include: External or outer ear, consisting of: Pinna or auricle. This is the outside part of the ear. External auditory canal or tube. This is the tube that connects the outer ear to the inside or middle ear. Tympanic membrane (eardrum). The tympanic membrane divides the external ear from the middle ear.
How We Hear Hearing Associates, Inc.
Helix: The outermost curvature of the ear, extending from where the ear joins the head at the top to where it meets the lobule. The helix begins the funneling of sound waves into the ear; Fossa, superior crus, inferior crus, and antihelix: These sections make up the middle ridges and depressions of the outer ear. The superior crus is the first ridge that emerges moving in from the helix.
HEARING ANATOMY AND PROCESS AUDIOLOGIS
Ear Anatomy, Diagram & Pictures | Body Maps Human body Head Ear Ear The ears are organs that provide two main functions — hearing and balance — that depend on specialized receptors called.

15.3 Hearing Anatomy & Physiology
The ear can be divided into three parts; external, middle and inner.This article will focus on the anatomy of the external ear - its structure, neurovascular supply and clinical correlations. The external ear can be divided functionally and structurally into two parts; the auricle (or pinna), and the external acoustic meatus - which ends at the tympanic membrane.

The Anatomy of the Outer Ear Health Life Media
Your inner ear is the last stop that sound waves make in a carefully orchestrated journey that starts from your outer ear. These waves travel from your outer ear through your middle ear to your inner ear. In the inner ear, the sound waves are converted into electrical energy, which your hearing nerve delivers to your brain as sound, making it.

Human Ear Anatomy Parts of Ear Structure, Diagram and Ear Problems
Here is a blank human ear diagram for you to label, so that you can memorize the different parts of this vitally necessary organ, for good.